Nickel : Properties, Uses, and Benefits
2025.02.19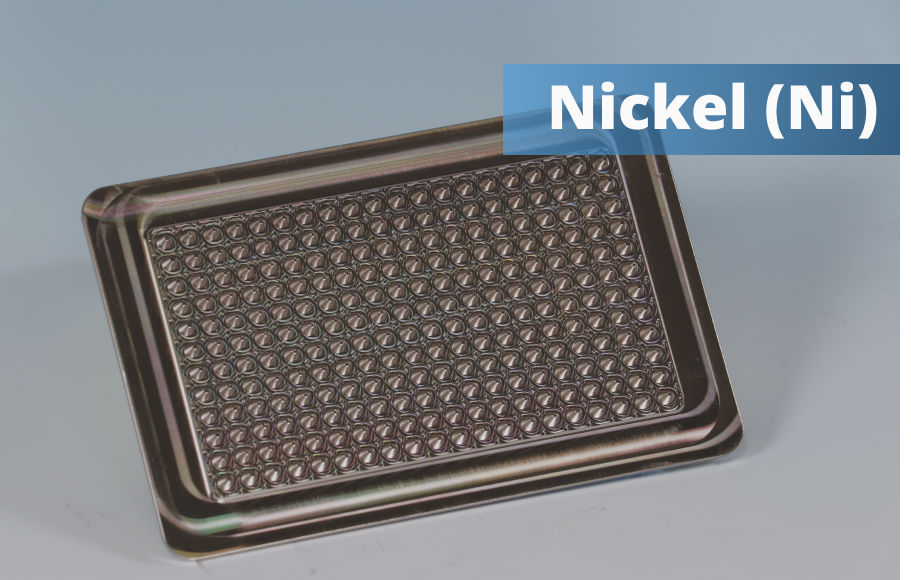
Nickel and its alloys are widely used in the manufacturing industry due to their excellent mechanical properties, corrosion resistance, and
high-temperature stability. These characteristics make nickel an ideal choice for producing mechanical components used in aerospace, automotive, and industrial applications.
Properties of Nickel
Nickel is a strong and durable metal known for its ability to withstand extreme conditions. Its key properties include:
-
High Strength and Toughness: Nickel-based alloys offer excellent tensile strength and durability, making them suitable for heavy-duty applications.
-
Corrosion Resistance: Pure nickel has high resistance to alkali and nitrogen gas, making it ideal for chemical processing equipment.
-
Heat Resistance: With a melting point of 1433°C, nickel maintains its mechanical properties at high temperatures, making it essential in heat-intensive environments.
-
Good Ductility and Workability: Despite its hardness, nickel can be machined with the right techniques and tools.
-
Magnetic Properties: Pure nickel exhibits high permeability, making it useful for electromagnetic applications.
-
Low Thermal Expansion: Specific nickel alloys, such as Invar and Kovar, have controlled thermal expansion properties for specialized applications.
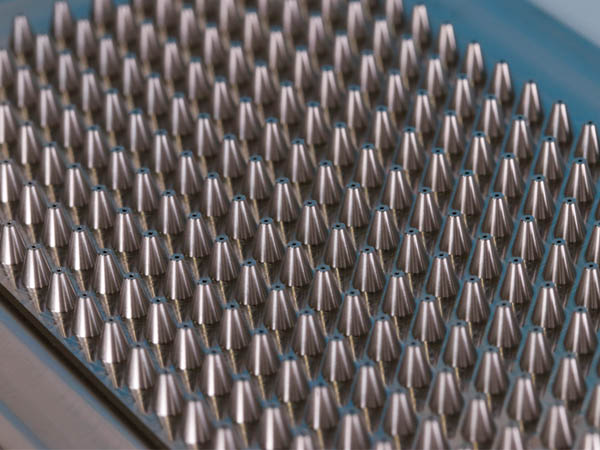
Notable Nickel Alloys
Nickel is often combined with other metals to form specialized alloys with unique properties:
-
Invar (36% Nickel, 64% Iron): Known for its nearly zero coefficient of thermal expansion at room temperature, making it ideal for precision instruments.
-
Super Invar: A variant with an even lower coefficient of thermal expansion than Invar, used in applications requiring extreme dimensional stability.
-
Kovar (29% Nickel, 17% Cobalt, 54% Iron): With a thermal expansion coefficient close to hard glass, Kovar is used for glass-to-metal sealing in electronics and ceramic bonding applications.
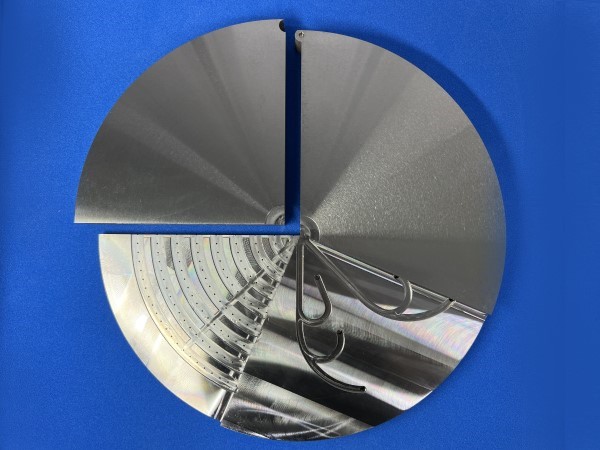

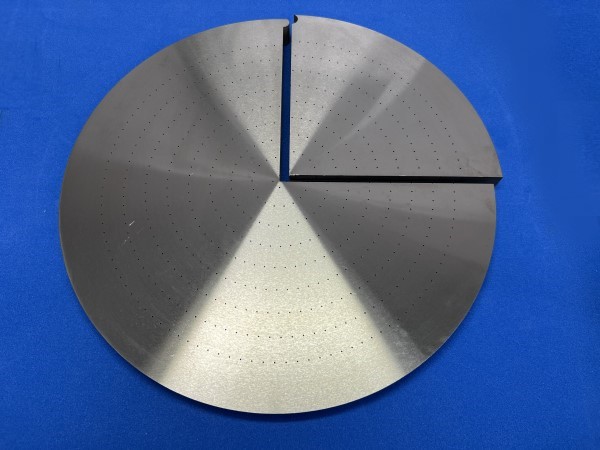
Front & Back side of Nickel-diffusion bonded product
Applications of Nickel in Mechanical Parts
Due to its superior properties, nickel is used in various industries:
-
Aerospace: Turbine blades, engine components, and structural parts.
-
Automotive: High-performance engine components and exhaust systems.
-
Energy Sector: Heat exchangers, piping, and nuclear power components.
-
Medical Industry: Surgical instruments and implants due to nickel’s biocompatibility.
-
Electronics: Components requiring precise thermal expansion properties, such as glass-to-metal seals.
-
Manufacturing Equipment: Used in caustic soda processing due to its high resistance to alkali and nitrogen gas.
-
Electromagnetic Applications: Radio wave shields and transducers, taking advantage of nickel’s magnetic properties.
Conclusion
Nickel is a valuable material in mechanical engineering due to its strength, corrosion resistance, and heat stability.
While machining nickel presents certain difficulties, using the right tools and techniques can optimize production efficiency.
With its widespread applications and specialized alloys, nickel remains an essential material for high-performance mechanical parts in various industries.
Would you like to discuss a project with us? Reach out today!




